Veganism, the exercise of abstaining from all animal products, has visible a surge in reputation. While imparting moral and environmental advantages, it additionally affords unique dietary demanding situations. Many misconceptions surround vegan diets, frequently main to concerns approximately protein deficiency, iron stages, and ordinary fitness. This article aims to dispel these myths and offer a complete manual for navigating a vegan lifestyle at the same time as making sure of nutrient consumption. By informing the potentially demanding situations and exploring the wealth of plant-based alternatives to be had, individuals can embody veganism with confidence and enjoy a healthful, pleasurable food plan.
Nutritional Challenges for Vegans
- Protein Deficiency Myth: A not-unusual misconception is that vegans struggle to fulfill their protein requirements. However, plant-based totally ingredients like lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, and seitan are exquisite protein resources. The key is to mix one-of-a-kind plant proteins to create complete amino acid profiles.
- Iron Deficiency: Iron is essential for oxygen shipping. While plant-based total iron (non-heme iron) is less problems absorbed than heme iron located in meat, foods like spinach, kale, and fortified cereals can offer good enough iron. Vitamin C complements iron absorption, so pairing those foods with citrus culmination or tomatoes is useful.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Essential for bone fitness, calcium, and vitamin D are often associated with dairy products. Fortunately, fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens, and tofu can be outstanding calcium assets. Vitamin D is normally produced with the aid of the skin via sunlight exposure, however, fortified plant-primarily based milk is another alternative.
- Vitamin B12: Exclusively found in animal merchandise, vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation. Vegans should rely upon fortified meals or supplements to fulfill their B12 desires. Nutritional yeast is a popular fortified option.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Important for heart health, omega-three fatty acids are plentiful in fish. However, plant-primarily based resources like flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts can provide alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3. While the body can convert ALA to the extra lively forms of omega-3s (EPA and DHA), the conversion performance is low.
Plant-Based Alternatives: A Nutritional Powerhouse

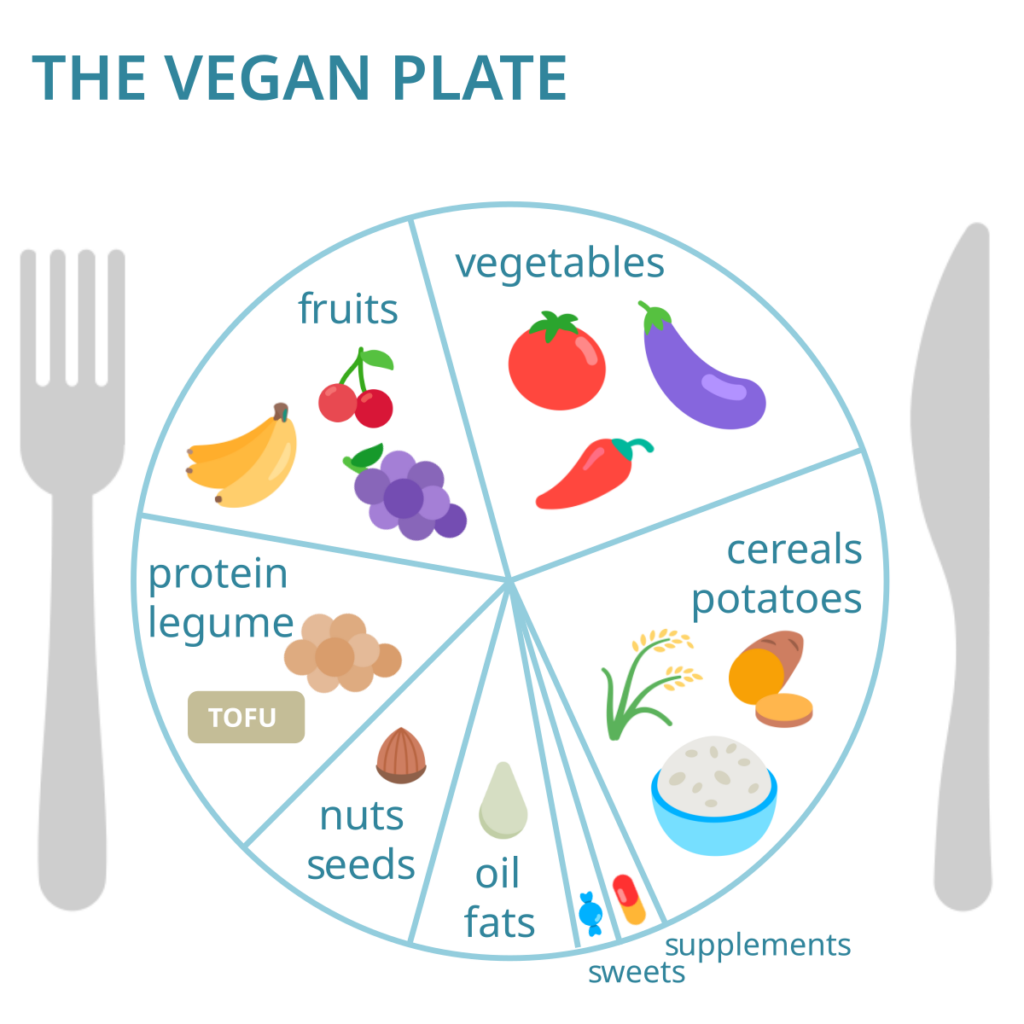
Contrary to popular belief, a vegan diet may be especially nutrient-wealthy. With careful plans, it’s feasible to consume all important vitamins without compromising on flavor or variety.
Protein-Rich Foods
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans, and black beans are exceptional protein resources. They additionally offer fiber, iron, and different vital vitamins.
- Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based merchandise are entire proteins, they incorporate all important amino acids. They are versatile and may be utilized in diverse dishes.
- Seitan: Made from wheat gluten, seitan is a high-protein meat opportunity with a chewy texture.
Iron-Packed Options
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in iron. Consuming them with vitamin C-rich ingredients enhances iron absorption.
- Fortified Cereals: Many plant-based totally cereals are fortified with iron to enhance their nutritional cost.
Calcium Sources
- Fortified Plant-Based Milk: Soy, almond, oat, and rice milk are regularly fortified with calcium.
- Leafy Greens: While not as concentrated as dairy, leafy greens like kale and broccoli provide calcium.
- Tofu: Some tofu products are fortified with calcium.
Vitamin D
- Fortified Plant-Based Milk: Many plant-primarily based milk options are fortified with Vitamin D.
- Sunlight Exposure: The body produces Vitamin D while exposed to daylight.
Omega-three Fatty Acids
- Flaxseed, Chia Seeds, and Walnuts: These plant-based totally foods are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a form of omega-three fatty acid.
Meal Planning and Tips

- Meal Planning and Tips for Vegans: Effective meal-making plans are critical for keeping a balanced vegan eating regimen. By incorporating quite a few plant-based meals and being mindful of nutrient intake, you can experience delicious and nutritious meals.
- Creating Balanced Vegan Meals: Prioritize fruits, greens, complete grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Try to incorporate unique plant-primarily based proteins in the day to ensure ok amino acid consumption. Opt for resources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Even with plant-primarily based meals, it’s important to hold portion control.
- Incorporating a Variety of Plant-Based Foods: Experiment with extraordinary plant-based totally elements to save your dietary boredom and make certain an extensive variety of vitamins. Explore diverse cuisines for inspiration.
- Importance of Food Fortification: Many plant-primarily based products are fortified with essential vitamins like calcium, diet D, and vitamin B12. Check labels to become aware of fortified alternatives.
Tips for Vegan Meal Prep and Cooking

- Batch cooking: Prepare big portions of grains, legumes, and sauces for shop time.
- Leftovers: Repurpose leftovers into new meals to lessen food waste.
- Experiment with flavors: Explore one-of-a-kind herbs, spices, and seasonings to beautify the taste of your dishes.
- Read labels cautiously: Be aware of hidden elements like honey or dairy derivatives.
With careful planning and a variety of plant-based options, you can thrive on a vegan diet. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance to meet your specific nutritional needs. You may also like other posts in our Health section.