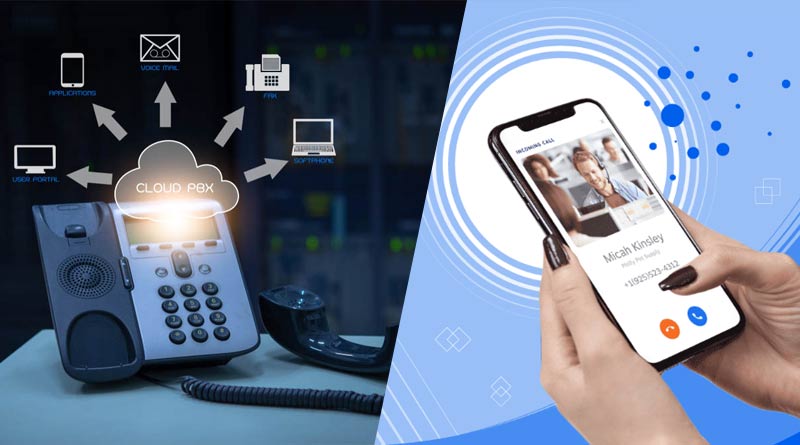
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology revolutionizes communication by enabling voice calls over the Internet instead of traditional telephone networks. This game-changing innovation transforms voice into data packets, transmitted seamlessly across digital networks. VoIP brings cost efficiency, flexibility, and a wealth of features like video conferencing and instant messaging. As we delve into the intricate realm of VoIP, we uncover the mechanics and benefits propelling this technology to the forefront of modern telecommunications, reshaping how individuals and businesses connect in the digital age. Join us on a journey through the wires and waves of VoIP innovation.
What is voice-over-IP (VoIP) Technology?
Forget copper wires, hello internet calls! VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a game-changer in communication. Imagine this: instead of relying on old-fashioned phone lines, VoIP lets you make calls using your internet connection. It works by transforming your voice into digital packets, similar to sending tiny data tidbits over the web. These packets then travel across the internet highway, reaching their destination and transforming back into clear audio for the person you’re calling. No extra phone lines needed, just crystal-clear calls using the internet you already have. Pretty cool, right? VoIP is a big reason why communication is becoming faster, easier, and more accessible worldwide.
How Voice-Over-Internet Protocol (VoIP) Work?
Voice-over-Internet Protocol (VoIP) works by converting analog audio signals, typically generated during voice communication, into digital data. This digital data is then transmitted over the internet in the form of data packets. The process involves several key steps:
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion: The voice signal from a microphone or telephone is initially converted from analog to digital format. This is typically done by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which samples the analog signal and converts it into a stream of digital data.
- Packetization: The digital voice data is segmented into small packets. Each packet contains a piece of the voice signal, along with additional information such as source and destination addresses.
- Internet Transmission: The packets are then transmitted over the internet using Internet Protocol (IP). This can occur over various types of networks, including broadband connections, Wi-Fi, or mobile networks.
- Digital-to-Analog Conversion: At the receiving end, the digital packets are reassembled and converted back into an analog signal. This is typically done by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
- Voice Playback: The reconstructed analog signal is then played through the speaker of the receiving device, such as a phone or computer, allowing the recipient to hear the voice of the caller.
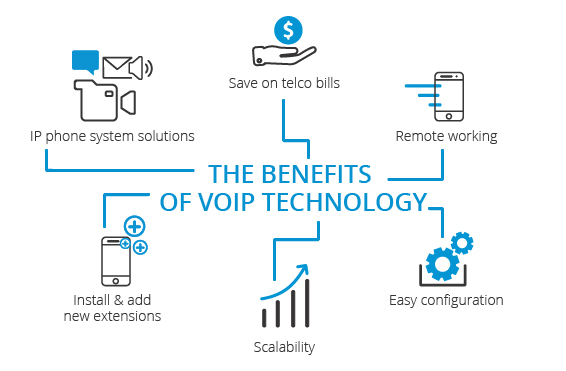
Advantages and Disadvantages of Voice-Over-Internet Protocol (VoIP)
Advantages of Voice-Over-Internet Protocol (VoIP):
- Cost Efficiency: VoIP often costs less than traditional phone services, especially for long-distance and international calls. By utilizing the internet, it eliminates the need for separate telephone lines, reducing overall communication expenses.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Users can make VoIP calls from any location with an internet connection, providing increased flexibility and mobility compared to traditional phone systems tied to specific physical lines.
- Scalability: VoIP systems can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate changes in business size or communication needs. This scalability makes it adaptable to evolving organizational requirements.
- Feature-Rich Services:“VoIP extends beyond traditional voice calls, offering additional features like video conferencing and instant messaging,” explained Sarah Thompson, a telecommunications specialist at TechWave Communications. “This enriches the communication experience and supports a variety of collaborative tools.”
- Unified Communications: VoIP facilitates the integration of various communication channels into a unified platform. Users can seamlessly switch between voice, video, and text communication within a single interface, promoting unified and efficient communications globally.
Disadvantages of Voice-Over-Internet Protocol (VoIP):
- Internet Dependency: The quality of VoIP calls is heavily dependent on a stable and high-speed internet connection. Poor connectivity can lead to dropped calls or reduced voice quality.
- Power Dependency: During power outages, VoIP systems may become non-functional unless there are backup power sources in place. Traditional phones can still operate during power failures.
- Emergency Service Limitations: VoIP may have challenges providing accurate location information during emergency calls (911). Traditional landlines are often associated with precise physical addresses for emergency services.
- Security Concerns: VoIP systems may be susceptible to security threats such as hacking and eavesdropping. Implementing measures like encryption and secure network configurations is necessary to mitigate these risks.
- Initial Setup Costs: While operational costs are generally lower, the initial setup of VoIP systems, including hardware and software, can involve significant expenses.
- Technical Expertise: Effective implementation and maintenance of VoIP systems may require technical expertise. Businesses may need to invest in training or hire specialists for system management.
While Voice-Over-Internet Protocol (VoIP) offers cost savings, flexibility, and feature-rich services, it demands a reliable internet connection and entails considerations for power outages, emergency services, and security. Understanding both the advantages and challenges is crucial for organizations seeking to embrace the transformative potential of VoIP technology. For more such posts please visit our Technology section.



